We learn about conditionals
In today's class we learned about conditionals, what are conditionals?
They describe the result of something that might happen (in the present or future) or might have happened but didn't (in the past) . They are made using different English verb tenses.
Another definition can also be "Conditional tenses are used to speculate about what could happen, what might have happened, and what we wish would happen. In English, most sentences using the conditional contain the word if. Many conditional forms in English are used in sentences that include verbs in one of the past tenses. This usage is referred to as "the unreal past" because we use a past tense but we are not actually referring to something that happened in the past. There are five main ways of constructing conditional sentences in English. In all cases, these sentences are made up of an if clause and a main clause. In many negative conditional sentences, there is an equivalent sentence construction using "unless" instead of "if"."
There are also four different types of conditionals.
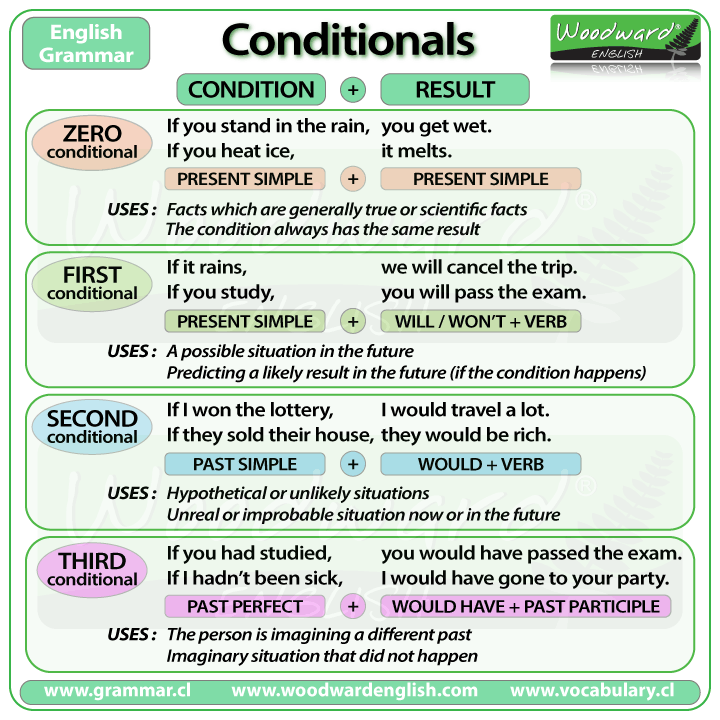
- The Zero Conditional: used for when the time being referred to is now or always and the situation is real and possible.
Form: (if + present simple, ... present simple)
Ex: If you heat water to 100 degrees, it boils.
- The First Conditional: used to refer to the present or future where the situation is real. Refers to a possible condition and its probable result.
Form: (if + present simple, ... will + infinitive)
Ex: If it rains tomorrow, we'll go to the cinema.
- The Second Conditional: used to refer to a time that is now or any time, and a situation that is unreal.
These sentences are not based on fact. Is used
to refer to a hypothetical condition and its probable result.
Form: (if + past simple, ... would + infinitive)
Ex: If I had a lot of money, I would travel around the world.
- The Third Conditional: is used to refer to a time that is in the past, and a situation that is contrary to reality.
The facts they are based on are the opposite of what is expressed. Is used to refer to an unreal past condition and its
probable past result.
Form: (if + past perfect, ... would + have + past participle)
Ex: If I had gone to bed early, I would have caught the train.
Comentarios
Publicar un comentario